O-Arm Navigation System: A new era of precision and safety in surgery!
O – Arm Navigation . Nowadays, the use of technology in medical science is growing so rapidly that it is enabling us to deliver results that were not even imaginable earlier. One such cutting-edge technology that enhances precision and safety in surgical procedures is the O-Arm Navigation System. This system acts as an ‘eyes’ for doctors during surgery, allowing them to see the complex structures inside the body in real-time.
Let us understand what this O-Arm Navigation System is, how it works, and what amazing benefits it has in the field of surgery.
What is O-Arm Navigation System?
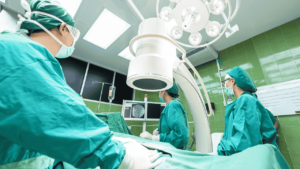
O-Arm Navigation System is an advanced 3D imaging system specially designed for the surgical environment. It is a mobile X-ray system capable of taking 2D and 3D images of the patient right in the operation theatre (OT). It is an ‘O’ shaped gantry that rotates around the patient and generates high-quality images from different angles.
These images are then connected to a computer navigation system. This navigation system provides the surgeon with a detailed 3D model of the patient’s anatomy, on which the surgeon can see the real-time position of his surgical instruments. Just like navigation (GPS) shows you the way on the road, this system shows the surgeon the way inside the body.
How does the O-arm navigation system work?
The functioning of the O-arm navigation system can be understood in a few steps:
3D Image Acquisition: Before or during the surgery, the O-arm device rotates around the part of the patient where the surgery is to be done (eg spine). It takes hundreds of 2D X-ray images in a single scan.
3D Reconstruction: These 2D images are immediately processed by a powerful computer and reconstructed into a detailed 3D volumetric model.
Integration with Navigation System: This 3D model is loaded into a surgical navigation system. The surgeon’s instruments (such as screw drivers, drills or probes) are attached to special sensors.
Real-time Tracking: The navigation system constantly tracks the position of these instruments and shows their exact position on the 3D image. This lets the surgeon know where his instrument is inside the body and in relation to which structure (such as vein, bone).
Key Benefits of O-Arm Navigation System.
The O-Arm Navigation System provides several key benefits in surgery:
Unmatched Accuracy:
It helps surgeons operate with precision in complex body parts, such as the spine or brain.
It ensures accuracy in the placement of screws or implants, reducing the risk of incorrect placement.
Example: In spine surgery, it ensures extreme accuracy when placing screws near nerves and the spinal cord, greatly reducing the chances of neurological damage.
Enhanced Safety:
Real-time 3D images allow surgeons to avoid damaging vital nerves, blood vessels and organs.
The need for repeated conventional X-rays is reduced, reducing radiation exposure to both the patient and the surgical team.
Improved Surgical Outcomes:
Increased accuracy increases the likelihood of successful surgery.
Reduced risk of complications leads to better and faster patient recovery.
In some cases, it makes minimally invasive surgery (MIS) possible, which allows for smaller incisions, less bleeding, and shorter hospital stays.
Time Efficiency:
Accurate images are immediately available during surgery, so the surgeon doesn’t have to wait for repeated X-rays.
This makes the surgical process more efficient, which can reduce operation time.
Helpful in Complex Cases:
In complex cases where the anatomy is not normal (such as deformity due to previous surgery or congenital abnormalities), the O-Arm System provides invaluable information.
Applications of O-Arm Navigation System.
O-Arm Navigation System is mainly used in surgical procedures where high accuracy and real-time imaging is required:
Spine Surgery: This is its most prominent use. It is very helpful in spinal fusion, screw placement, decompression surgery and scoliosis correction.
Neurosurgery: Removal of brain and spinal cord tumors or in other complex neurological procedures.
Orthopedic Surgery: Repair of complex fractures, especially pelvic











Post Comment